Publications
From curious minds to groundbreaking discoveries—your gateway to scholarly excellence
From curious minds to groundbreaking discoveries—your gateway to scholarly excellence
 Read More
Read More This opinion article explores the evolving responsibilities of data scientists in the current data-driven landscape, in which ethical, privacy, and governance standards have grown considerably in importance.
 Read More
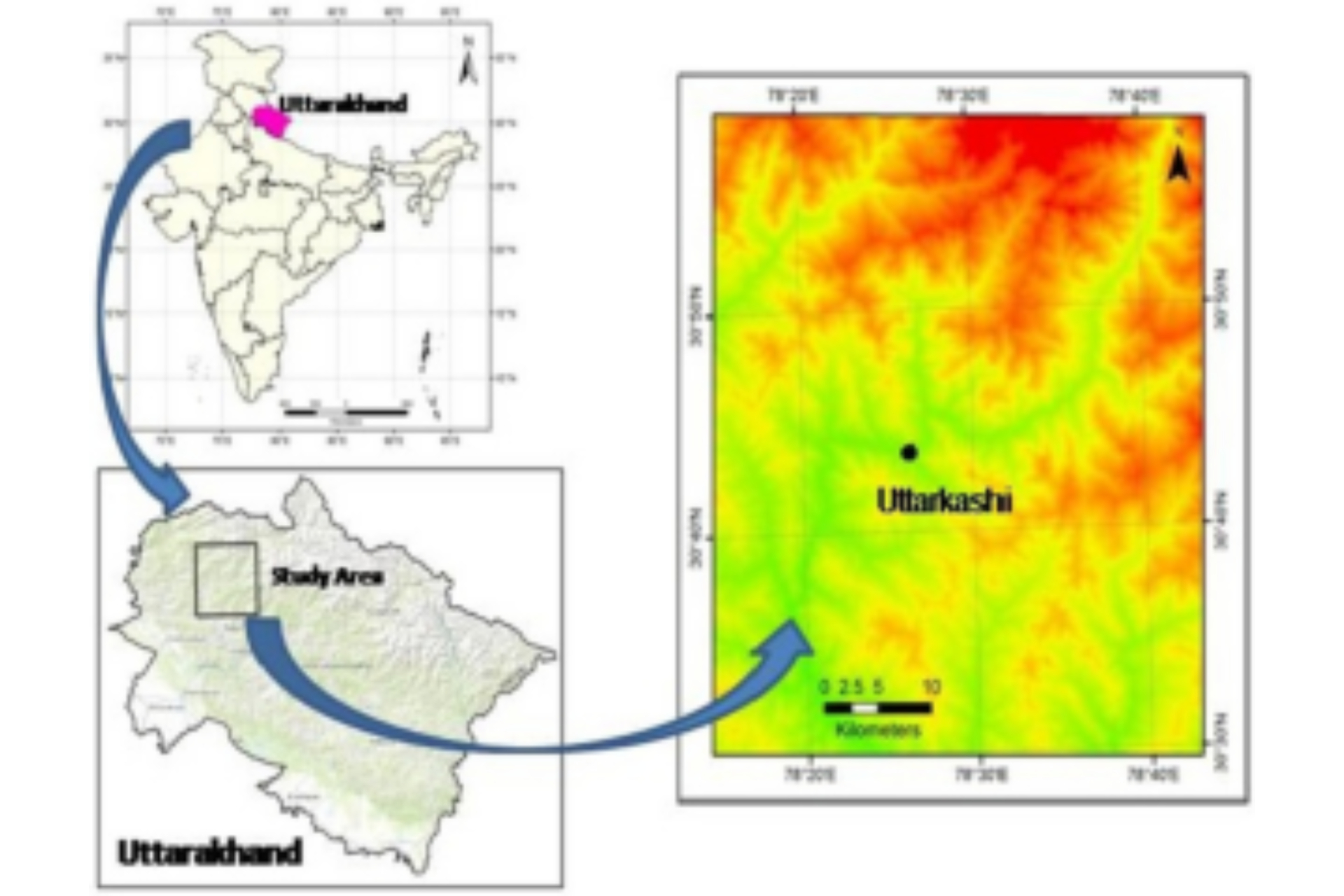
Read More The purpose of this study is to develop a landslide susceptibility prediction model by applying the Frequency Ratio (FR) model and remote sensing data sets for the Northern part of Uttarakhand, India.
 Read More
Read More The metalloid arsenic (As) induces oxidative stress is a well-known fact. However, the extent of variation of oxidative stress according to different exposure levels of As.
 Read More
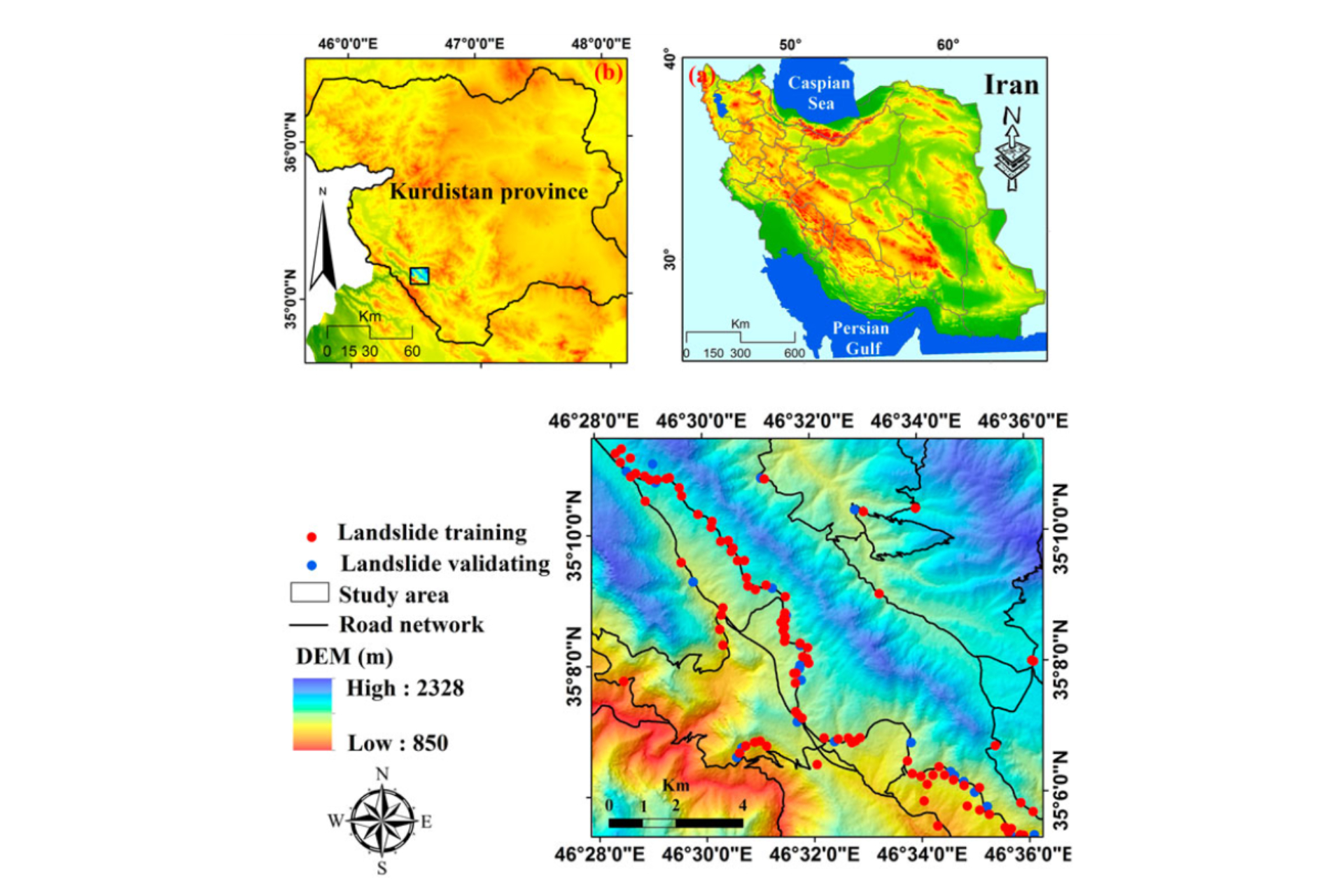
Read More Landslides can be a major challenge in mountainous areas that are influenced by climate and landscape changes.
 Read More
Read More Soil erosion is a major cause of damage to agricultural lands in many parts of the world and is of particular concern in semiarid parts of Iran. We use five machine learning techniques.
 Read More
Read More This study evaluates state-of-the-art machine learning models in predicting the most sustainable arsenic mitigation preference.